admin
Latest posts by admin (see all)
- Wart Cream: Which One to Choose? - October 14, 2019
- Wart Freeze: How Does the Cryodestruction Take Place? - October 11, 2019
- How to Use Salicylic Acid for Warts Removal? - October 8, 2019
Plantar wart is a firm and flat formation on the skin of the foot, somewhat elevated above its level and covered with a layer of keratinized epithelium. Plantar warts are 34% of all warts. The main method for the diagnosis of plantar warts is dermatoscopy. The location of the wart on the sole leads to permanent injury and pain when walking. For this reason, the plantar wart often requires treatment, although it can go away on its own. Learn more about the distinctive features of a plantar wart to make sure that you have exactly this type of warts. This will help you to choose the correct treatment course.
Contents
- Manifestations of Plantar Wart
- Diagnosis of a Plantar Wart
- The First Symptoms of Plantar Warts in Children
- How to Identify a Plantar Wart in a Child?
- Can Plantar Wart Cause Any Complications?
Manifestations of Plantar Wart
The plantar wart is a firm, well-defined seal on the sole. Most often, it has an oval or rounded shape and is about 1-2 cm in size. The formation of 1-3 mm protrudes above the general level of the skin. The skin color in the plantar wart is usually not changed but may be light brown or pink.
The surface of the wart at the beginning of its formation is smooth. Over time, it becomes covered with layers of dead epidermis, it becomes rough and becomes gray-yellow. Sometimes, in the center of the plantar wart there is a crater-like depression. Black and brown spots, which can often be seen on the surface of the wart, are caused by thrombosis of the surface capillaries.
As a rule, the plantar wart is single. The appearance of daughter warts indicates a high activity of the virus. Multiple warts attach a mosaic pattern to the affected area of the sole, for which they were called “mosaic warts.”
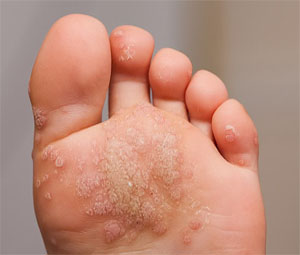
There may be an independent disappearance of the plantar wart. In this case, there is no trace left on the skin of the foot. But more often, due to constant injury, self-wart does not occur. Not painful by itself, it begins to cause the patient considerable discomfort and even sharp pain associated with friction and pressure of the wart on the sole of the shoe.
Diagnosis of a Plantar Wart
In appearance, the plantar wart often resembles a callus or a patch of cutaneous hyperkeratosis. Only a professional dermatologist can distinguish it from these formations. For this, dermatoscopy is performed. In order to better investigate a new formation, the doctor pre-scrapes the upper layers of the cornified epithelium. The absence of a skin pattern on the surface of the formation and the identification of the characteristic symptom of “thrombosed capillaries” speak in favor of the plantar wart. Positive results of PCR diagnostics for HPV confirm the infection of the patient.
To determine the germination depth of the plantar wart, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound of the skin. If a malignant nature of the formation is suspected, a consultation of a dermato-oncologist is carried out. In identifying deformities and diseases of the foot, it is necessary to consult a podologist.
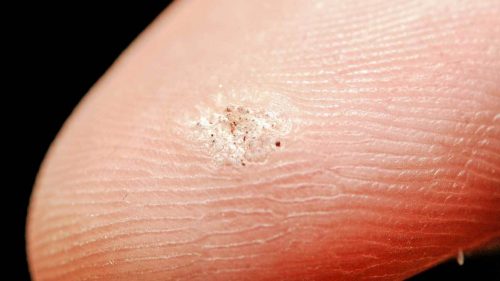
Plantar wart is usually differentiated from keratoderma of the soles and palms in people with the Reiter’s syndrome. The smaller size of the formation, not conical, but a flat shape, the symptom of “thrombosed capillaries” and the absence of inflammatory changes around the stratum corneum make it possible to distinguish the plantar wart from keratoderma. Palmar-plantar syphiloids have some similarities with plantar wart. They are distinguished from the latter by their multiple character, painlessness and characteristic arrangement in the form of rings or arcs, and a positive RPR test for syphilis.
The First Symptoms of Plantar Warts in Children
The main manifestation of plantar warts in childhood is the occurrence of a dense round neoplasm on the back of the palm or foot. The main symptom of this disease is itching during walking. At the initial stage of the disease: there is a miniature “callus”, which begins to itch, it aches a bit when walking. After 2-4 weeks, the primary symptoms change to secondary: a rough lump appears in the center of the “corn”, black spots may appear in the central part of the wart, the edges of the wart are surrounded by keratinized skin.
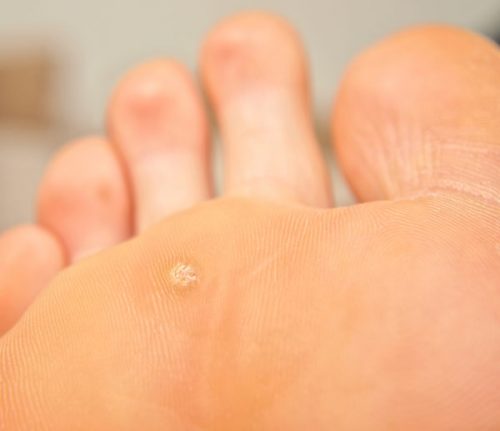
How to Identify a Plantar Wart in a Child?
The diagnosis of plantar wart can be identified by a specialist only. A professional dermatologist can diagnose a plantar wart in a child. This is due to the fact that the ugly plantar warts often resemble a corn. Only a doctor can distinguish a wart from a corn. The dermatologist uses the following methods to diagnose and detect the disease:
- dermatoscopy,
- PCR diagnostics,
- HPV diagnostics.
In some cases, it is necessary to determine how deep the tumor is. To this end, the doctor may prescribe: an ultrasound scan, consultation with a dermato-oncologist (if the dermatologist suspects that there is a malignant tumor behind the plantar wart).
Can Plantar Wart Cause Any Complications?
It makes sense to talk not about the complications of the disease as such, but about the complication of the treatment of plantar warts. The following factors affect the presence of negative consequences and their degree: the individual characteristics of the child’s body, the well-being of the child, the number of warts, the place of their dislocation, the wart removal tool, and the qualifications of a specialist.
What can complicate the elimination of plantar warts: damage to the skin surrounding the neoplasm, scarring, recurrence of the disease (if the child has weak immunity), it is extremely rare, but nevertheless there is a rebirth of benign warts to malignant tumors.
